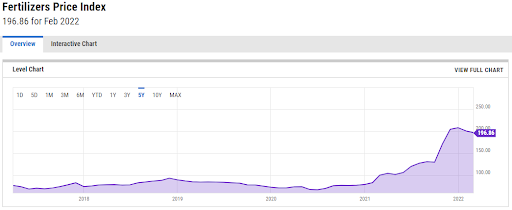
(introduction of pilot applications not only in the Pilsen region)
The seminar takes place on April 28, 2022 in the Úhlava Education Center, o.p.s. in Klatovy, Plánická 174
Program:
9.00 – 9.10 Opening and welcoming of participants – Úhlava, o. P. S.
9.10 – 9.30 Presentation of the project MANDOLIN and DIH – World – Tomáš Mildorf and Kristýna Čerbová, Plan4all z.s.
Working with satellite data
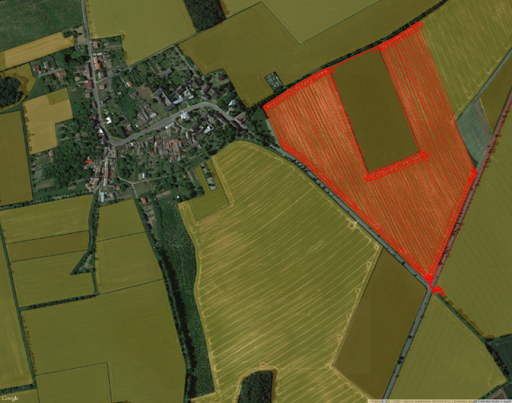
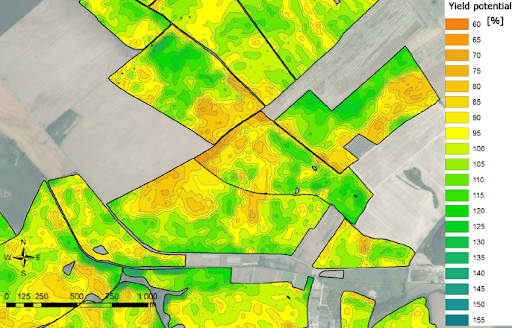
9.30 – 9.50 Sentinel 2 and Sentinel 1 data processing for agriculture (What data can bring us, what are the problems and benefits) – Heřman Šnevajs and Karel Charvát, WirelessInfo
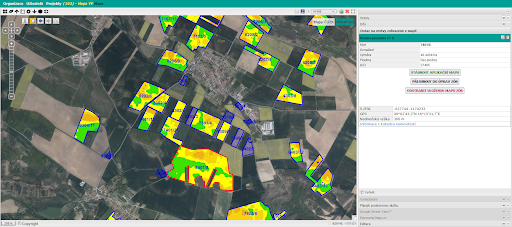
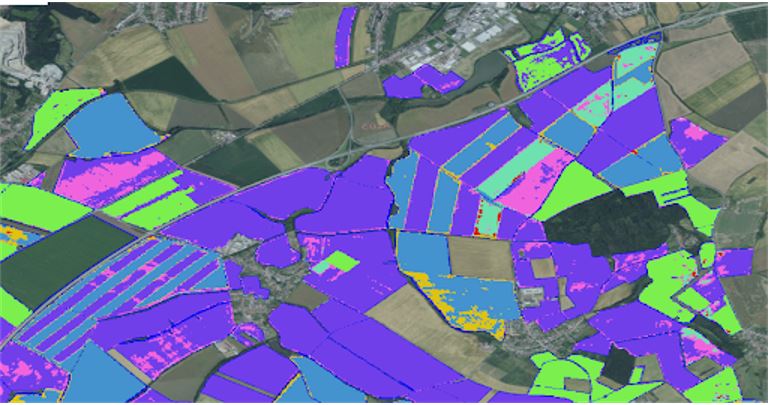
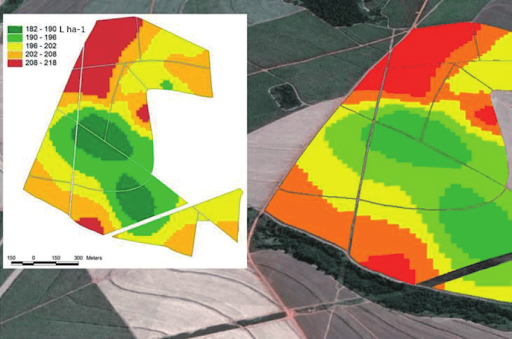
9.50 – 10.00 Generate your own zones – Jan Macura, Wirelessinfo / Dmitrij Kožuch, Plan4All z.s.
10.00 – 10.15 How to ensure the sharing and sale of satellite products using blockchain technology – Jiří Kvapil, Lesprojekt – služby, s.r.o.
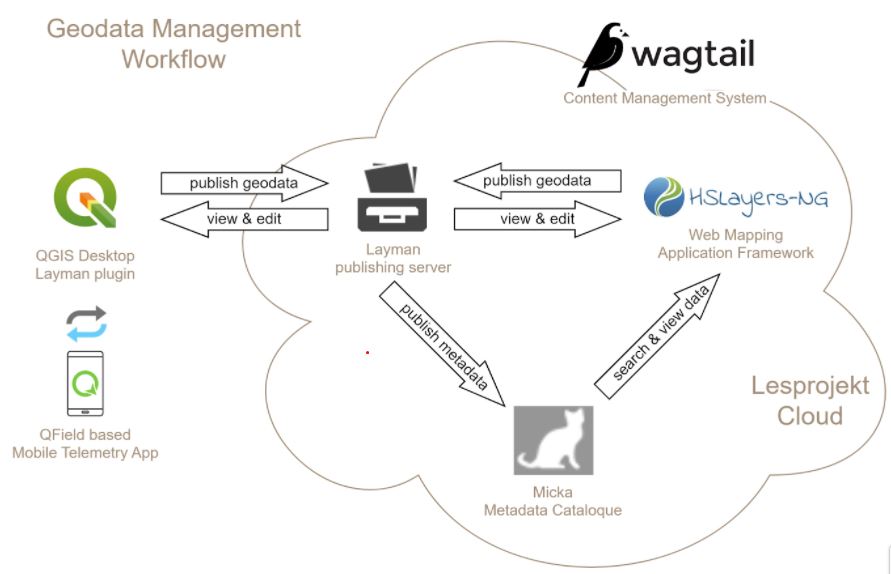
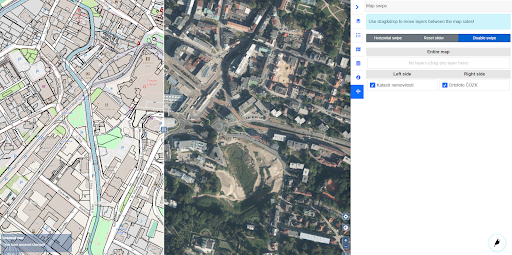
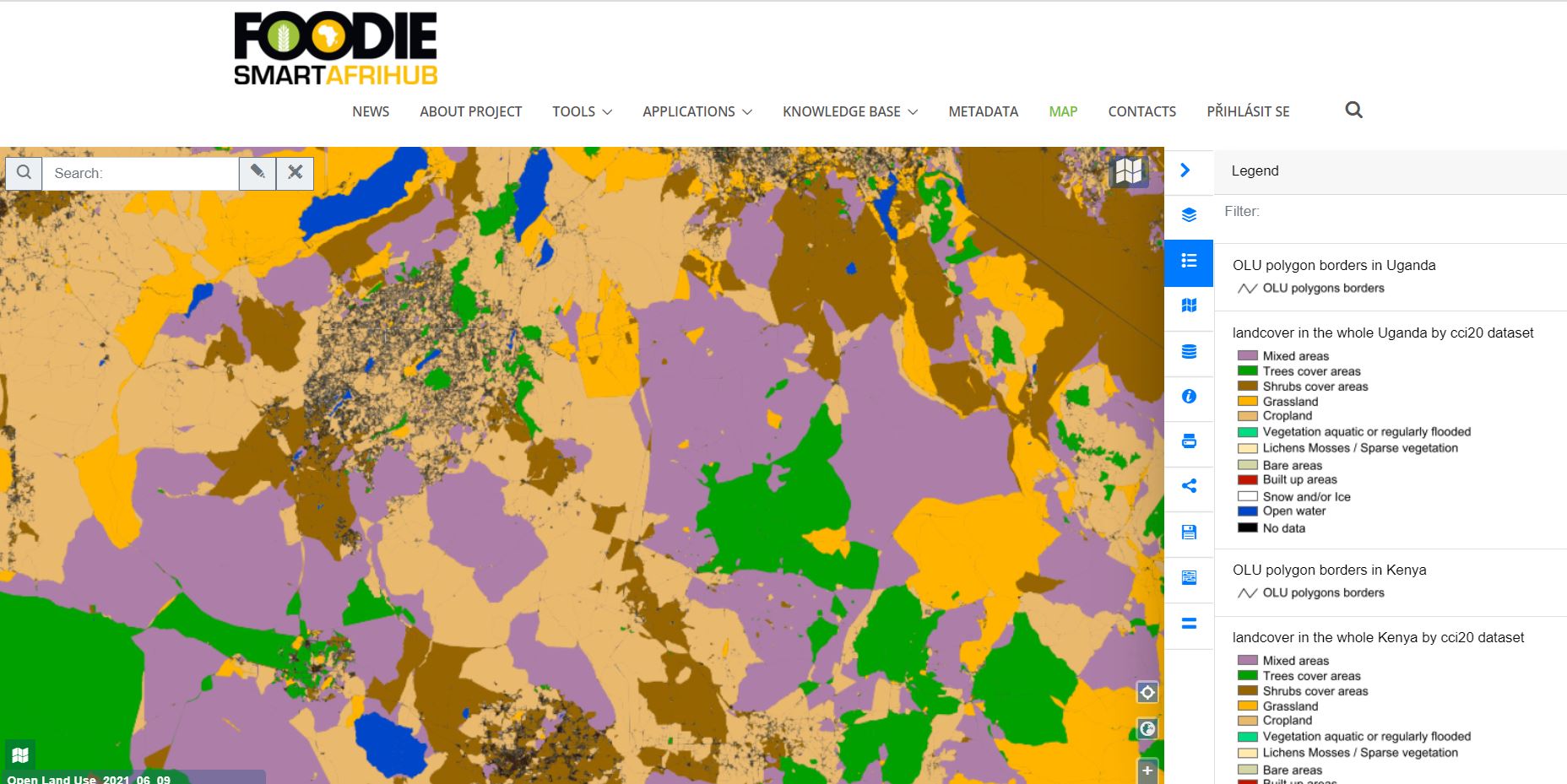
10.15 – 10.45 FarmINSIDER – a platform that integrates research results and methods into an application for end users – Karel Charvát jr., Lesprojekt – služby, s.r.o.
10.45 – 10.55 coffee break
Working with sensors
10.55 – 11.10 Presentation of used solutions in agriculture and food transport – Jaroslav Šmejkal, Lesprojekt – služby, s.r.o.
11.10 – 11.30 Hardware solutions in agriculture and food transport – Agronode and Teltonika – Marek Musil, Czech Open Solutions Center spol. s r.o. and Jaroslav Šmejkal, Lesprojekt – služby, s.r.o.
11.30 – 11.40 Senslog – solution for sensor data collection – Michal Kepka, UWB in Pilsen
11.40 – 12.00 Applications for working with sensors (IE20, Dashboard) – Michal Kepka, UWB in Pilsen
12.00 – 12.20 refreshment break
Support for local sales
12.20 – 12.35 Regional specialties and Atlas of regional specialties – Petr Horák, WirelessInfo
12.35 – 12.45 Sales of regional specialties (e-shop) – Radana Šašková, Úhlava, o.p.s., and Tomáš Zelený, Šumavaprodukt, s.r.o.
12.45 – 13.00 What’s next? – Karel Charvát WirelessInfo
The seminar is intended for owners, managers and other managers and organizational staff of agricultural enterprises, producers and distributors and food trade workers with their own logistics. Due to the current pandemic situation, some contributions may be presented online.
Please do not forget to register to participate.
The seminar is held with the financial support of the DIH-World project funded under the European program H2020, grant agreement No. 952176