Moving Big and Open Data and Open Source into Practice.
(Agriculture, areal planning, biodiversity, climate change adaptation, water-energy-food nexus, transport, logistic)
A cooperation between professionals, project teams including students, freelancers and start-ups.
RESULTS
The jury members Marie-Françoise Voidrot (Open Geospatial Consortium), Martin Pelikan (Czech University of Life Sciences in Prague) and Ondrej Svab (Czech Ministry of Transport) awarded the following winning teams:
- 1st place: Big Data for Fishery by Karel Jedlicka, Dmitrij Kozuch, Petr Uhlir
- 2nd place: Extension and Enrichment of SPOI Knowledge Base by Raul Palma, Otakar Čerba, Stein Runar Bergheim, Raitis Berzins
- 3rd place: Delimiting Agro Zones by Marcela Doubkova, Apurva Kochar, Karel Jedlička, Karl Gutbrod, Vojtech Lukas, Michal Kraus
Congratualutions!
Source: PEF CZU Prague
WHEN
23 – 24 January 2018
WHAT
We would like invite you to join us in Prague and try together with others demonstrate possibilities of use of Big and Open Data and Open Source in real life application focused mainly on rural regions.
WHY
Today’s society relies on an easy, reliable and quick access to environmental information in order to manage challenges such as sustainable development, urbanization, climate change, and disaster risk. This information is provided by various organisations and initiatives. Both the public and private sectors thus produce and publish data and information covering the needs within areas such as agriculture, forestry, fishery, environmental protection, landscape planning and natural risks and hazards management. People engaged in local community activities are able to capture local knowledge with the use of multimedia such as videos, photos and different kinds of sensor data. The collected information can contribute to tackle environmental and societal challenges in food production, forestry, fishery, risk management, air, soil and water pollution and contamination, landscape management, education and commercialisation.
Needless to say, data and information varies in quality, have different formats, granularity, time resolution and so on. With the advent of satellite technology, web, and mobile technology, we are producing vast amount of data often described as big data.
Volunteered geographic information (VGI) is the harnessing of tools to create, assemble, and disseminate geographic data provided voluntarily by individuals. Recent developments in the sensor domain have led to a DIY (Do It Yourself) approach, using sensors based on low cost hardware, as well as an increasing availability of Bluetooth connected sensors that can be easily connected to a smartphone and together with existing smartphone sensors provide a large amount of spatio-temporal sensor data. Citizen observatories are community-based environmental monitoring and information systems. They build on innovative and novel Earth observation applications embedded in portable or mobile personal devices. This means that citizens can help and be engaged in observing our environment. Young generation representing smartphone users is one of the enablers of new geographic information based applications. Spatial information helps young generations to learn about relations to and with the environment, history and culture in different regions.
Online sharing of spatial information goes beyond the linguistic barriers, which are one of the most important constraints for the communication between different regions. The open data movement covers many issues of using existing data sets without any limits or restrictions. Open data activities mean open-source, open-content and open-access. Open data sets are often provided by governmental bodies, but also by scientists or international organisations and bodies (e.g. European Commission, World Bank, Copernicus, Group of Earth Observations).
PARTICIPATION
The main objective of the Prague INSPIRE Hack is to create a meeting place for professionals, regional and national project team members including students, start-ups, freelancers, current and future users and investors to move scientific results into practice. The focus will be on Big Open Data:
- Earth Observation
- Sensors data
- VGI data
- GNSS technologies
- Linked Open Data
applied in the agriculture and rural development sectors. The first phase of the Prague INSPIRE Hack starts with creating teams connecting different types of stakeholders. You are invited to create your own team with people you know or people you’ve worked with before. Or, you can explore the existing ideas and teams that have been already created and you can simply join them. In any case, you need to register in order to gain access to the shared space where team building and design of ideas is happening. The team building will start already before Prague INSPIRE Hack using online and offline communication tools
HOW
For participation, please register at https://goo.gl/forms/GfJrnhAldqwO5avi1
As soon as you register, you will be sent a link to the shared collaboration space. In this space you will be able to join the already existing teams and projects or you can create your own team and project idea. Please, keep the shared space up-to-date and share the basic information about your team and project idea as well as your contact information and means of communication. The workspace will be accompanied by data and tools, which are available in preliminary versions, listed at the end of this page/document. We will offer introduction webinars and other supporting material
WHERE
The Prague INSPIRE Hack is an INSPIRE Hackathon. These hackathons start with virtual meetings and activities some weeks before a face-to-face meeting ends the hacking process. The awards ceremony concludes the hackathon. The Prague INSPIRE Hack starts by forming teams and suggesting ideas on a dedicated space made available after registration the 15th December 2017.
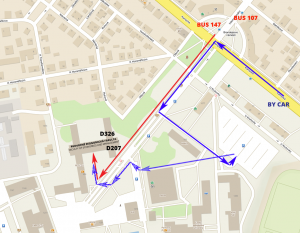
The face-to-face segment of the Prague INSPIRE Hack 2018 will take place at Faculty of Economics and Management Czech University of Life Sciences Prague (https://www.pef.czu.cz/en/ ), Kamýcká 129, Praha Suchdol, Czech Republic on 23rd and 24th January 2018.
Accommodation options
Hotel Galaxie – about 700 meters from the meeting place
http://www.hotelgalaxie.cz/en/contact
Dormitory at the campus
https://www.kam.czu.cz/en/r-10440-accommodation/r-10459-dormitory-jih
AWARDS
Student Award
The Prague INSPIRE Hack offers a financial award (400 Euro) for the two best applications developed by students using one or more of the new tools: HSLayers NG, DAP, Mobile HSLayers NG or SensLog or by using at least one of the data sets from: Smart Point of Interests, Open Land Use, Open Transport Map.
Prague INSPIRE Hack Awards
The best three projects from other applicants will be selected by the jury that will be formed during January 2018 and the winning teams will be awarded. This includes a live broadcast on social media, an interview (video/audio) with the winning team that they can use freely and that will be published in specified channels. The most creative use of a combination of INSPIRE compliant open data including space-based, in-situ, and citizen science/crowdsourced data will be awarded the INSPIRE Hackathon Award.
EO ClimLab Award
The best project design innovative service or product derived from EO data to solve the societal challenges that appeared due to climate change influence, will be awarded the EO ClimLab Award.
IMPORTANT DATES
| 15 December 2017 | Start of the registration |
| 15 December 2017 – 22 of January 2018 | Building teams for hackathon projects |
| 22 January 2018 | Deadline for team registration online. additional teams could be established during the hack |
| 23 January 9 00 | Opening of Hack |
| 9 15 – 10 00 | Ideas pitches |
| 10 00 – 12 00 | Team building |
| 12 00 – 18 00 | Hacking |
| 12 00 – 18 00 | Parallel workshops |
| 24 January 9 00 – 14 00 | Hacking |
| 09 00 – 15 00 | Parallel training workshops |
| 14 00 – 15 00 | Presentation of results |
| 15 00 – 15 30 | Jury decision |
| 15 40 – 17 00 | Final ceremony with a glass of wine |
WORKSHOPS
In the frame of the Prague INSPIRE Hackathon, several workshops will be organised. The following workshops are currently foreseen:
- Tuesday 23 Jan 2018, 12:00 – 13:00 Francisco Buján (CARSA) Invitation to the WATIFY Matchmaking event May 2018 in Tuscany around the topic of sustainable precision agriculture. It will address technologies such as Big Data, IoT/sensoring and Earth Observation.
- Tuesday 23 Jan 2018, 13:00 – 14:00 Ondrej Svab (Ministry of Transport of the Czech Republic) Opportunities in ESA programmes.
- Tuesday 23 Jan 2018, 14:00 – 15:00 Marek Aldorf How (ESA BIC Prague) to start business in space, focused on business opportunity, models and incubation activities in Space
- Tuesday 23 Jan 2018, 15:00 – 16:30 Karel Charvat will organise workshop on the theme: “Horizon 2020 as an opportunity to elaborate your ideas”, which will be focused on open and coming calls (2018 and 2019) related to subject of Hackathon. It will be connected with small networking and anybody, who is interested could provide also 3 minutes presentation of ideas or partner search
- Wednesday 24 Jan2018, 10:00 – 11:00 Tomas Reznik will organise a workshop “Metadata without showing a specialized metadata platform: GeoDCAT and other (meta)data semantic approaches“
Participation at workshops is free and open also for people not taking directly part in the hacking activities. Registration is however required at https://goo.gl/forms/GfJrnhAldqwO5avi1.
CONTACT
For any inquiries please contact Karel Charvat at: charvat(at)ccss.cz and Tomas Mildorf at: mildorf(at)centrum.cz
ORGANISERS AND SUPPORTERS
 Department of Information Technologies (DIT) has been involved in the field of teaching and scientific research, collaborates with business, governments, and domestic and foreign universities. It participates in many domestic and international projects and is part of international teams tackling applied research. Its focus puts DIT among the most prolific departments of Faculty of Economics and Management Czech University of Life Sciences Prague (http://kit.pef.czu.cz/en/ ).
Department of Information Technologies (DIT) has been involved in the field of teaching and scientific research, collaborates with business, governments, and domestic and foreign universities. It participates in many domestic and international projects and is part of international teams tackling applied research. Its focus puts DIT among the most prolific departments of Faculty of Economics and Management Czech University of Life Sciences Prague (http://kit.pef.czu.cz/en/ ).
 Plan4all (https://www.plan4all.eu/) – Plan4all is a non-profit association sustaining and further enhancing the results of multiple research and innovation projects. It aggregates large open datasets related to planning activities in different specialisms areas transport, spatial and city planning, environment and tourism. Plan4all makes sure that open data are easily accessible for reuse, data are maintained and their quality is improved.
Plan4all (https://www.plan4all.eu/) – Plan4all is a non-profit association sustaining and further enhancing the results of multiple research and innovation projects. It aggregates large open datasets related to planning activities in different specialisms areas transport, spatial and city planning, environment and tourism. Plan4all makes sure that open data are easily accessible for reuse, data are maintained and their quality is improved.
 ESA BIC Prague – The ESA Business Incubation Centre Prague initiative offers an extensive support package to entrepreneurs and young start-ups with innovative ideas for exploiting space systems, technologies or patents in order to develop their non-space businesses on Earth. During the period of 5 years, 25 Czech start-ups have opportunity to discover potential use of space technologies in daily life. CzechInvest agency as the programme operator, with support of the City of Prague, Ministry of Industry and Trade and European Space Agency will mediate an incubation package to selected applicants which will contain consultancy services in technology and business areas. Start-ups will also have marketing support as well as help finding their partners and potential investors. ESA BIC Prague is co- organising Prague Hack in frame of EO ClimLab project where the role is to organise and support international and local knowledge and innovation events (e.g. FabSpace, Start- up weekend, Act In Space, etc.) EOVations, which could be described as EO innovation-oriented competitions. The objective of these events is to encourage developers, users and business people to work together on multidisciplinary, societal and business challenges focused on climate change. http://www.esa-bic.cz/
ESA BIC Prague – The ESA Business Incubation Centre Prague initiative offers an extensive support package to entrepreneurs and young start-ups with innovative ideas for exploiting space systems, technologies or patents in order to develop their non-space businesses on Earth. During the period of 5 years, 25 Czech start-ups have opportunity to discover potential use of space technologies in daily life. CzechInvest agency as the programme operator, with support of the City of Prague, Ministry of Industry and Trade and European Space Agency will mediate an incubation package to selected applicants which will contain consultancy services in technology and business areas. Start-ups will also have marketing support as well as help finding their partners and potential investors. ESA BIC Prague is co- organising Prague Hack in frame of EO ClimLab project where the role is to organise and support international and local knowledge and innovation events (e.g. FabSpace, Start- up weekend, Act In Space, etc.) EOVations, which could be described as EO innovation-oriented competitions. The objective of these events is to encourage developers, users and business people to work together on multidisciplinary, societal and business challenges focused on climate change. http://www.esa-bic.cz/
 CSITA (Czech Society for Information Technology in Agriculture – https://www.csita.cz/en ) nongovernment organization was founded in 2002 for the purpose of supporting development and use of ICT in agrarian sector (agriculture, forestry, water management, environment, food environment and manufacturing industry) and in countryside in general (in rural regions). The aim of CSITA organization is mainly:
CSITA (Czech Society for Information Technology in Agriculture – https://www.csita.cz/en ) nongovernment organization was founded in 2002 for the purpose of supporting development and use of ICT in agrarian sector (agriculture, forestry, water management, environment, food environment and manufacturing industry) and in countryside in general (in rural regions). The aim of CSITA organization is mainly:
- Meetings, conferences, seminars, trainings and workshops management and support for publication of members´ activities results.
- Research, advisory and consultancy activities in area of ICT in agrarian sector and in rural regions.
- Promoton and support of Open Research.
- Support for educational activities focused on the area of applied informatics.
- Promotion and support of Open Education.
- Expanse of useful SW and HW applications.
International cooperation has been realised primarily by active membership in EFITA (European Federation for Information Technology in Agriculture, Food and the Environment), cooperation and shared knowledge with national members of EFITA and its partner organizations: AFITA (Asian Federation for Information Technology in Agriculture), PanAfita(Pan-American Federation for Information Technology in Agriculture), INFITA (International Network for Information Technology in Agriculture) and others.
 DataBio (http://databio.eu/) – The data intensive target sector selected for the DataBio project is the Data-Driven Bioeconomy, focusing in production of best possible raw materials from agriculture, forestry and fishery/aquaculture for the bioeconomy industry to produce food, energy and biomaterials taking into account also various responsibility and sustainability issues. DataBio proposes to deploy a state of the art, big data platform “on top of the existing partners” infrastructure and solutions – the Big DATABIO Platform. The work will be continuous cooperation of experts from end user and technology provider companies, from bioeconomy and technology research institutes, and of other partners. In the pilots also associated partners and other stakeholders will be actively involved. The selected pilots and concepts will be transformed to pilot implementations utilizing co-innovative methods and tools where the bioeconomy sector end user experts and other stakeholders will give input to the user and sector domain understanding for the requirements specifications for ICT, Big Data and Earth Observation experts and for other solution providers in the consortium.
DataBio (http://databio.eu/) – The data intensive target sector selected for the DataBio project is the Data-Driven Bioeconomy, focusing in production of best possible raw materials from agriculture, forestry and fishery/aquaculture for the bioeconomy industry to produce food, energy and biomaterials taking into account also various responsibility and sustainability issues. DataBio proposes to deploy a state of the art, big data platform “on top of the existing partners” infrastructure and solutions – the Big DATABIO Platform. The work will be continuous cooperation of experts from end user and technology provider companies, from bioeconomy and technology research institutes, and of other partners. In the pilots also associated partners and other stakeholders will be actively involved. The selected pilots and concepts will be transformed to pilot implementations utilizing co-innovative methods and tools where the bioeconomy sector end user experts and other stakeholders will give input to the user and sector domain understanding for the requirements specifications for ICT, Big Data and Earth Observation experts and for other solution providers in the consortium.
EO ClimLab (http://eoclimlab.eu) – EO ClimLab (Earth Observation Climate Laboratory) is a project organised by the ESA (European Space Agency) for central Europe. The ESA aspires to foster the next generation of EO data-driven digital start-ups in Europe. In order to initiate the development of a European network of such start-ups, the project would provide innovative EO-based information services addressing climate resilience. The EO ClimLab is a collaborative research e-environment enabling the rapid development and prototyping of new Earth Observation (EO)-based products aiming to support adaptation and mitigation to climate change across multi-disciplinary societal and business themes (e.g. agriculture, health, risk management, infrastructure maintenance, education, outreach).
NextGEOSS (http://nextgeoss.eu/) – The NextGEOSS project will implement a federated data hub for access and exploitation of Earth Observation data, including user-friendly tools for data mining, discovery, access and exploitation. This data hub will be supported by a strong commitment to the engagement of Earth Observation and related communities, with the view of supporting the creation of innovative and business oriented applications. The main general objectives for NextGEOSS are to 1) Deliver the next generation data hub and Earth Observation exploitation for innovation and business; 2) Engage communities, promoting innovative GEOSS powered applications from Europe; and 3) Advocate GEOSS as a sustainable European approach for Earth Observation data distribution and exploitation. NextGEOSS engages main providers of Earth Observation data, including Copernicus Collaborative Ground Segments and Core Services.
SKIN – (Short Food Supply Chains Knowledge and Innovation Network) – is an ambitious initiative of 20 partners in 14 countries in the area of Short Food Supply Chains (SFSCs). It intends to systematise and bring knowledge to practitioners, promote collaboration within a demand-driven innovation logic and provide inputs to policymaking through links to the EIP-AGRI.
Partners will scout, analyse and classify a significant number of cases in different countries. “Good practices” (at least 100) will be systematised, processed into highly usable formats and made accessible to stakeholders via the web and through the set-up of regional nodes, to allow a deeper penetration of existing knowledge into practice. The work on good practices will also allow identifying key issues (hindrances or opportunities) around SFSCs. Such issues will be the main themes of 6 “innovation challenges workshops” the purpose of which is to stimulate stakeholders to propose new ideas for innovation based research or innovation uptake. These will be supported in a coaching phase where consortium partners deliver guidance to stakeholders for the full development of those innovative ideas.
 EUXDAT – Agriculture is a, literally, vital industry. Not only important for nourishment, but also a key determinant of health, economic and political stability; employment; business and biological ecosystems; and society. Because of its importance, most attention focuses on productivity but it is essential to have a global view in order to address environment sustainability problems. EUXDAT proposes an e-Infrastructure, which addresses agriculture, land monitoring and energy efficiency for a sustainable development, as a way to support planning policies. In order to do so, we need to address the problems related to the current and future huge amount of heterogeneous data to be managed and processed. EUXDAT builds on existing mature components for solving them, by providing an advanced frontend, where users will develop applications on top of an infrastructure based on HPC and Cloud. The frontend provides monitoring information, visualization, different parallelized data analytic tools and enhanced data and processes catalogues, enabling Large Data Analytics-as-a-Service. EUXDAT will include a large set of data connectors (UAVs, Copernicus, field sensors, etc.), for scalable analytics. As for the brokering infrastructure, EUXDAT aims at optimizing data and resources usage. In addition to a mechanism for supporting data management linked to data quality evaluation, EUXDAT proposes a way to orchestrate tasks execution, identifying whether the best target is a HPC center or a Cloud provider. It will use monitoring and profiling information for taking decisions based on trade-offs related to cost, data constraints, efficiency and resources availability.
EUXDAT – Agriculture is a, literally, vital industry. Not only important for nourishment, but also a key determinant of health, economic and political stability; employment; business and biological ecosystems; and society. Because of its importance, most attention focuses on productivity but it is essential to have a global view in order to address environment sustainability problems. EUXDAT proposes an e-Infrastructure, which addresses agriculture, land monitoring and energy efficiency for a sustainable development, as a way to support planning policies. In order to do so, we need to address the problems related to the current and future huge amount of heterogeneous data to be managed and processed. EUXDAT builds on existing mature components for solving them, by providing an advanced frontend, where users will develop applications on top of an infrastructure based on HPC and Cloud. The frontend provides monitoring information, visualization, different parallelized data analytic tools and enhanced data and processes catalogues, enabling Large Data Analytics-as-a-Service. EUXDAT will include a large set of data connectors (UAVs, Copernicus, field sensors, etc.), for scalable analytics. As for the brokering infrastructure, EUXDAT aims at optimizing data and resources usage. In addition to a mechanism for supporting data management linked to data quality evaluation, EUXDAT proposes a way to orchestrate tasks execution, identifying whether the best target is a HPC center or a Cloud provider. It will use monitoring and profiling information for taking decisions based on trade-offs related to cost, data constraints, efficiency and resources availability.
 PoliVisu – Policy Development based on Advanced Geospatial Data Analytics and Visualisation. is a Research and Innovation project designed to evolve the traditional public policy making cycle using big data. The aim is to enhance an open set of digital tools to leverage data to help public sector decision-making become more democratic by (a) experimenting with different policy options through impact visualisation and (b) using the resulting visualisations to engage and harness the collective intelligence of policy stakeholders for collaborative solution development.
PoliVisu – Policy Development based on Advanced Geospatial Data Analytics and Visualisation. is a Research and Innovation project designed to evolve the traditional public policy making cycle using big data. The aim is to enhance an open set of digital tools to leverage data to help public sector decision-making become more democratic by (a) experimenting with different policy options through impact visualisation and (b) using the resulting visualisations to engage and harness the collective intelligence of policy stakeholders for collaborative solution development.
The Prague INSPIRE Hack is a part of the INSPIRE Hackathon movement (link to INSPIRE Hackathon mission statement, also with a river ith tributaries image to illustrate how other hackathons contributes or are part of the “INSPIRE hackathon movement”,making the output or results from the hackathon sustainable, or contribute to the sustainability of the results….
TOOLS FOR REUSE
Micka (http://micka.bnhelp.cz/) – Open Micka is a web application for management and discovery geospatial metadata. It is
- OGC Catalogue service (CSW 2.0.2)
- Transactions and harvesting
- Metadata editor
- Multilingual user interface
- ISO AP 1.0 profile
- Feature catalogue (ISO 19110)
- Interactive metadata profiles – management
- WFS/Gazetteer for defining metadata – extent
- GEMET thesaurus built-in client
- INSPIRE registry built-in client
- OpenSearch
- INSPIRE ATOM download service – automatically creation from metadata
INSPIRE CKAN extensions (https://github.com/CCSS-CZ/ckan-ext-inspire) – These extensions are designed for work with INSPIRE metadata in CKAN.
There are two modules:
Inspire_harvester – This module extends csw_harvester and spatial_metadata extensions to support harvesting of all INSPIRE required metadata elements from CSW 2.0.2 ISO AP 1.0.
Inspire_theme – This extension enables: Display INSPIRE metadata user friendly form at CKAN interface. Export INSPIRE metadata in extended GeoDCAT-AP 1.0 RDF format.
WebGlayer (http://webglayer.org/) / WebGLayer is JavaScript, WebGL based library for coordinated multiple views visualization. The library is focused on spatial data and large datasets (up to hundreds of thousands of features).
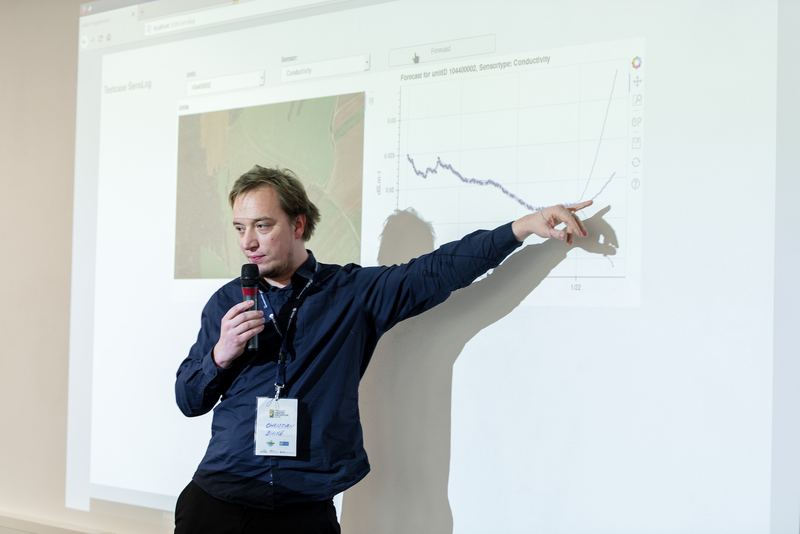
SensLog (http://www.senslog.org/) – SensLog is solution for static as well as mobile sensors and VGI. SensLog is web-based sensor data management system. SensLog is a solution that is suitable for static in-situ monitoring devices as well as for mobile devices with live tracking ability.
General tasks of SensLog can be summarized in following points:
- Receives measured data either directly from sensor device or indirectly from any Front-End Elements;
- Stores sensor data in SensLog data model implemented in RDBMS;
- Pre-processes data for easier querying if necessary, and/or analyzes sensor data;
- Publishes data through system of web-services to other Front-End Elements, or to other applications.
SensLog provides system of web-services exchanging messages in JSON format or provides standardized services using core methods of OGC SOS version 1.0.0. The latest version of REST API is following CRUD schema.
HSLayers NG + CESIUM (https://github.com/hslayers/hslayers-ng) HSlayers NG is a web mapping library written in Javascript. It extends OpenLayers 3 functionality and takes basic ideasn from the previous HSlayers library, but uses modern JS frameworks instead of ExtJS 3 at the frontend and provides better adaptability. That’s why the NG (“Next Generation”) is added to its name. It is still under development and provided as open source. HSLayers is built in a modular way which enables the modules to be freely attached and removed as far as the dependencies for each of them are satisfied. The dependency checking is done automatically. Core of framework is developed using AngularJS, requireJS and Bootstrap. This combination of frameworks was chosen mainly for providing fast and scalable development and for providing modern responsive layout of application. Cesium is an open-source JavaScript library for world-class 3D globes and maps. Our mission is to create the leading 3D globe and map for static and time-dynamic content, with the best possible performance, precision, visual quality, platform support, community, and ease of use.
HSlayers Cordoba (https://github.com/hslayers/cordova) Support of mobile platforms is important feature of HSL-NG development. Desktop HSL have responsive design but we are also working on special mobile application using Apache Cordova framework. Current version brings big part of HSL functionality (e.g. compositions, layer manager, search). One of goals is to enable collection of data in terrain (VGI) for projects based on HSL-NG.
You can check current code on Github or test first version on Android device with Google Play (other platforms won´t be supported in current development phase).
WebGlayer (http://webglayer.org/) / WebGLayer is JavaScript, WebGL based library for coordinated multiple views visualization. The library is focused on spatial data and large datasets (up to hundreds of thousands of features).
NiMMbus (http://www.opengis.uab.cat/nimmbus) – NiMMbus is solution for storing geospatial resources on the MiraMon cloud. NiMMbus is contributed to the hackaton as a geospatial user feedback storing tool. The system implements the Geospatial User Feedback standard developed in the OGC (and started in the FP7 GeoViQua project). This implementation in it using an API developed in the H2020 NextGEOSS The system allows to creating a citation of an external resource and then associate feedback about it. More information on how to use it and how to integrate in a metadata catalogue it can be seen at the https://github.com/joanma747/nimmbus.
Data Analytics Platform for climate resilience (DAP) (https://platform.eoclimlab.eu) The EO ClimLab Data Analytics Platform is a collaborative research environment ingesting, processing, storing and disseminating data and metadata. It provides a new innovation area enabling development of new Earth Observation services, algorithms, software and applications aiming to support adaptation and mitigation to climate change across multi-disciplinary societal and business themes (e.g. agriculture, health, risk management, infrastructure maintenance, education, outreach). The platform is available for everyone interested in climate change issues.
A virtual infrastructure environment on the cloud including:
- Data from EO satellites, with focus on ESA missions,
- Open Data from local providers and IoT sensors,
- Processing and storage capabilities,
- Tools for visualisation, programming and processing,
- Development Tool Kits (e.g. IoS, Android.)
Data available
The Smart Points of Interest data set (http://sdi4apps.eu/spoi/) is the seamless and open resource of POIs that is available for other users to download, search or reuse in applications and services. Its principal target is to provide information as Linked data together with other data set containing road network.
Open Land-Use Map (http://sdi4apps.eu/open_land_use/)is a composite map that is intended to create detailed land-use maps of various regions based on certain pan-Europen datasets such as CORINE Landcover, UrbanAtlas enriched by available regional data.
The Open Transport Map (http://opentransportmap.info/) displays a road network which
- is suitable for routing
- visualizes average daily Traffic Volumes for the whole EU
- visualizes daytime related Traffic Volumes
Talking technical, the Open Transport Map
- can serve as a map itself as well as a layer embedded in your map
- is derived from the most popular open dataset – OpenStreetMap
- is accessible via both GUI and API
- covers the whole European Union