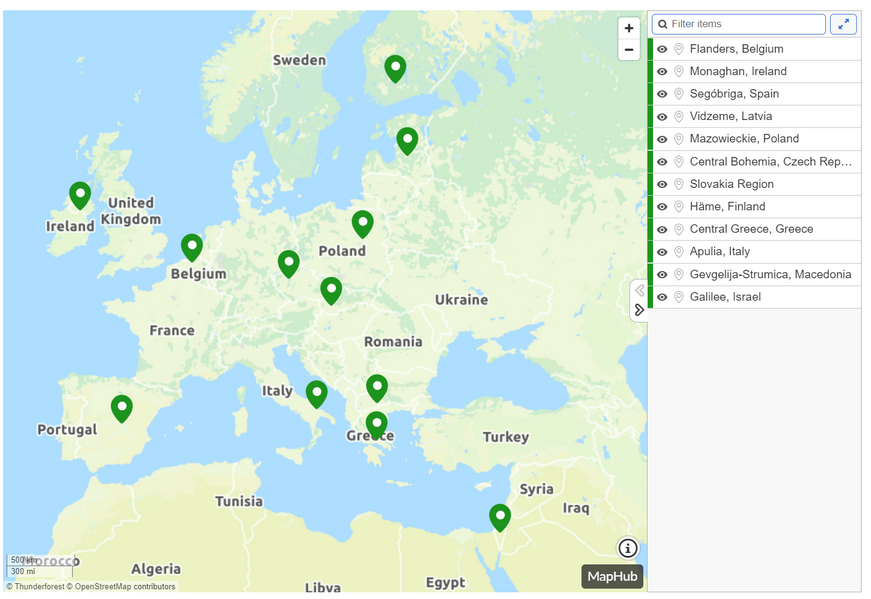
Since the inception of map whiteboard challenge and the first draft release in summer, various improvements have been made to the software parts enabling whiteboard functionality. This document will summarize the developments since that time. The current working prototype of the integrated system runs at https://dih.bosc.lv/modeller/private/ and is available for authorized users. The system’s purpose is to provide the user the possibility to create system dynamics models with linked spatial information in a form of map composition for each graph or model.
Whiteboard library and server configuration
Server architecture
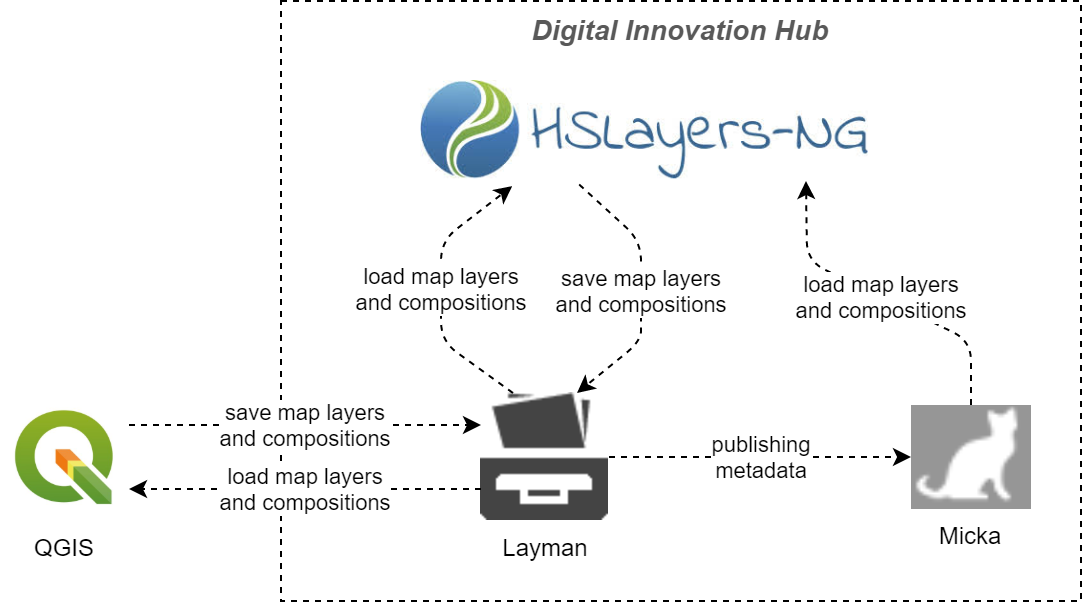
A docker based environment has been setup to run the components in production (see the diagram).
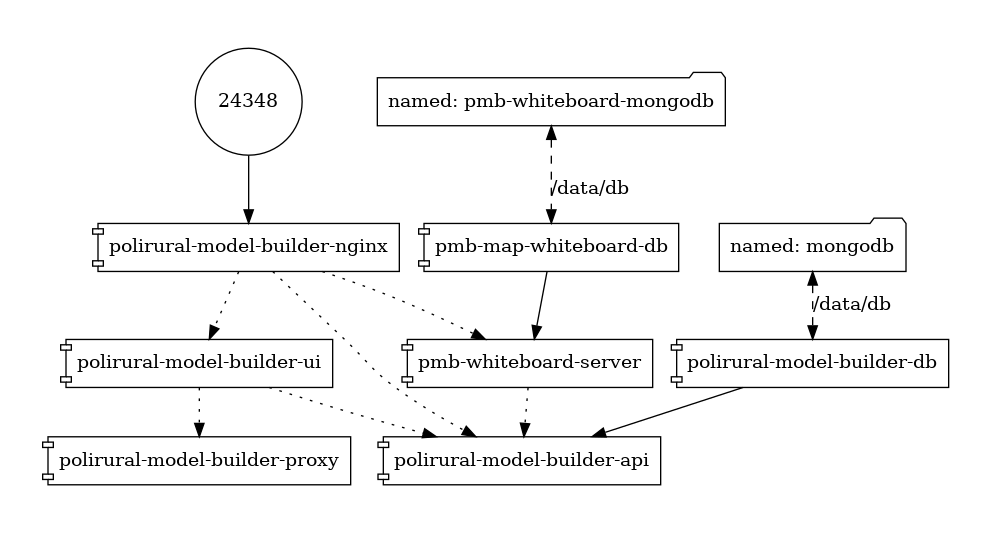
It consists of 2 mongo databases – one for the container application (Polirural modeller) and one for map whiteboard. Similarly we use 2 rest api endpoints named polirural-model-builder-api and pmb-whiteboard-server where the whiteboard-server supports both REST and Websocket protocols. At the top resides an nginx proxy to rule them all.
The map whiteboard server connects to model-builder-api provided GRAPHQL endpoint to validate user sessions and get the current users info. This is used as an alternative to OAUTH2, but conceptually does the same thing.
Client architecture
On the client side we have an Angular9 based application, which incorporates a map window component based on HSLayers-ng. Since it runs Openlayers under the hood, we can integrate the Map whiteboard library using the underlying Openlayers map object.
Since Hslayers already provides feature drawing functionality we have added to map whiteboard library the possibility to turn off the drawing toolbar not to have duplicate user controls and call the whiteboard libs data synchronization methods directly from javascript using hooks in hslayers. Also switching the current edited layer on mapwhiteboard library from outside needed to be created since the application supports multiple editable vector layers which are done on hslayers side.
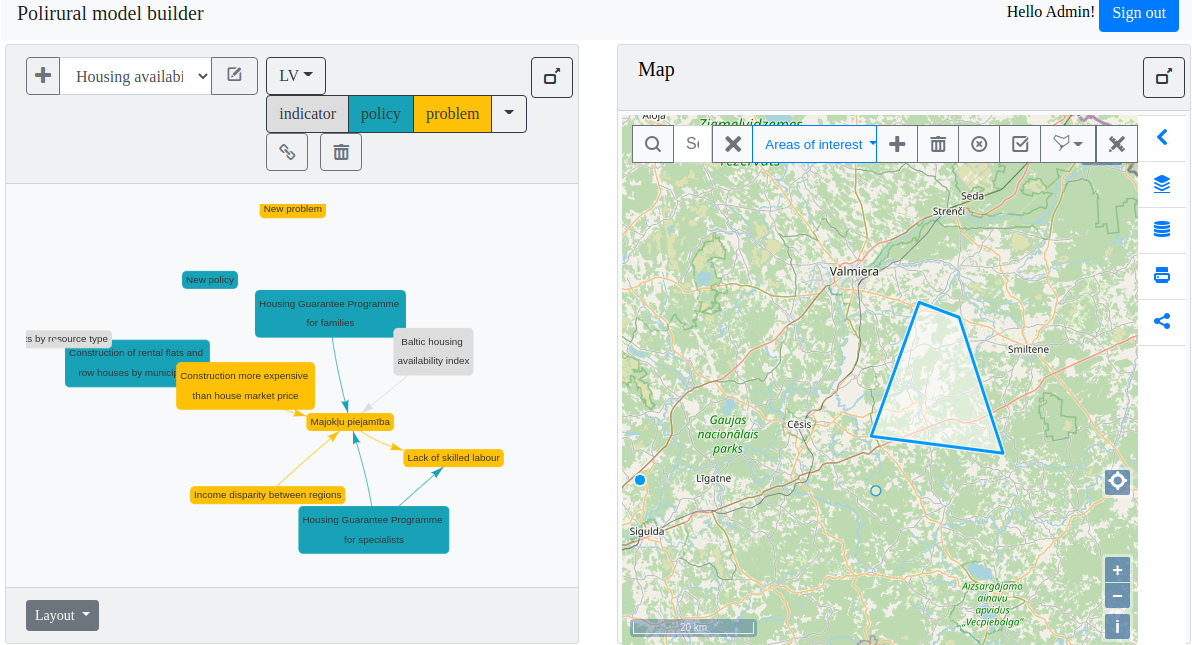
Map composition preparation
The map composition creation is still done in the application outside map whiteboard lib with the help of hslayers-ng, because it supports multiple layer types and parameters. The json serialize map object or individual layer is then passed to map whiteboard client side code, which then sends it to the server. This happens at the moment when the user selects a ‘Model’ in the dropdown list on the top-left corner of the UI. The software then checks if a map composition is linked to the model and creates it in case it doesn’t exist. In case it already exists the composition is being queried from the map whiteboard server, and layers are populated on the map including the features.
Recently we also developed an initial user rights model to keep track of who can access and edit the compositions.
The uploaded composition is stored on the harddrive, parsed and the title, description and filename of the composition is stored in Mongo database.
Downloading map composition file was developed (currently without embedded features)
Currently functionality for editing the composition supports:
- Add new layers either drawable vector or wms, arcgis or vector data loaded from external files
- Listing of editable layers parsed from composition file
- Requesting features for particular layers. Multiple editable layers are now supported
- Listing of my uploaded compositions for current user
- Granting access (owning) rights to the uploader of composition.
Still needs developing:
- Granting and removing access rights to additional users. Currently all users can see and edit the composition only they don’t appear in the list of compositions he/she owns.
- Renaming of layers.
- Deleting of composition (available to owner).
- Styling of features
- Activation of scratch layer
- Serialization of layers and composition on the map-whiteboard side.
Features
Whenever a user draws a feature, they are propagated to all the clients currently using the same composition meaning they selected the same ‘Model’ in the dropdown. Features are now linked to particular composition and layer, where previously we had a single fixed editable layer per composition. The features are stored in mongo databases and modification of them is done through CRUD operations on the Websockets API.
Listing of features is done for a specific editable layer by its title through REST API.